Project Steering: Explanation, Tasks and Methods
| Translated by Julian Hammer
Project steering is a central part of project management and comprises all activities aimed at keeping the actual values of a project, such as deadlines, costs or results as close as possible to the planned project specifications. It plays a decisive role during project implementation by continuously comparing planned and actual values in order to recognize deviations at an early stage and initiate targeted measures.
What is the difference between project steering and project management? In contrast to project management which bears overall responsibility for the project, project steering focuses on operational implementation and control.
While the project manager defines the objectives, assumes responsibility for planning and leads the team, the focus of project steering is on the monitoring and adjustment of time and budget plans, quality assurance as well as risk and change management.
The role of project management and project steering can be combined or they can be performed separately by different persons or bodies.
A key component of project management is regular planned/actual comparison. It allows for a close monitoring of the progress of a project and ensures that deviations are identified at an early stage. The most important methods that provide support include milestone trend analysis, earned value management and structured risk management. These tools help to visualize progress, evaluate costs and schedules and control risks proactively.
In addition, project steering is supported by the use of modern project management software . Such tools centralize planning, monitoring and communication, increasing efficiency and ensuring more precise control. Ultimately, project management plays a key role in successfully implementing complex projects on time, within budget and with the desired quality.
In our article, we take a closer look at the definition of project steering, show the difference between project steering and project management, provide information on the most important project steering methods and give tips on how the right tools can simplify project steering.
What is project steering?
Project steering means the systematic controlling and adjustment of all project-related processes, to ensure compliance with the objectives in terms of time, costs and quality. It entails the continuous monitoring of planned and actual values, the identification of deviations and the implementation of respective countermeasures. The objective is to coordinate operative processes efficiently and ensure project success through targeted controlling.
Typical areas of application for project management are complex construction projects, IT projects, product development and infrastructure programs. It acts as an interface between project management, clients and executing teams to ensure smooth communication and implementation.
The difference between project steering and project management is particularly evident at the level of responsibility. While the overall responsibility for the project resides with the project management, project steering is focused on its operative implementation. The project controller is responsible for controlling and monitoring and proposes appropriate measures in the event of deviations. However, he/she does not make any independent strategic decisions.
Project steering is indispensable, since it creates transparency, minimizes risks and contributes to the achievement of objectives through targeted controlling. Without consequent controlling, projects can easily fall outside the planned framework, which can lead to delays, cost overruns or defects in quality. It is therefore a decisive success factor for successful project implementation.
What project steering definitions and standards are there?
Project management is defined and interpreted in various standards, whereby all approaches aim to monitor and control projects efficiently and purposefully.
The most common standards are:
- DIN 69901
- PRINCE2
- PMBOK Guide
Each of them offers specific perspectives and methods for project steering.
DIN 69901 defines the term project steering as one of the five phases or main tasks of project management. According to DIN 69901, project steering means the operative steering of a project which is focused on coordination, monitoring and adjustment of time, cost and performance objectives.
It regards project steering as a sub-process of project management which ensures compliance with a defined framework. DIN attaches particular importance to structuring and clear responsibilities. According to DIN, controlling is not an isolated process component.
In PRINCE2 (Projects in Controlled Environments), project steering is defined as an independent process that is to be clearly distinguished from other management processes. The “Controlling a Stage” process is designed to control each project phase independently.
Within this process, progress is reviewed, deviations are identified and measures are initiated before the next phase can begin. Each phase ends with a formal review and a steering decision by the steering committee, which decides on the continuation of the project. This phase-related separation of the control system distinguishes PRINCE2 significantly from DIN 69901.
The PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) Guide defines project steering as part of the “Monitoring and Controlling” process group that is continuously applied throughout the entire project life cycle. In contrast to DIN 69901, project steering is not explicitly understood as an independent function here, but rather as an activity that is carried out by the project manager and relevant stakeholders. It includes the recording and evaluation of deviations and the initiation of measures to keep projects in line with time, costs and quality targets.
Here, standardized tools such as Earned Value Management, KPI Tracking and Change Management are used to ensure precise controlling.
Unlike PRINCE2 which organizes controlling based on phases, controlling in the PMBOK Guide is a continuous, dynamic process which is particularly suitable for projects that require flexible adjustment and continuous control.
Despite the differences in these approaches, there are also clear similarities: All standards emphasize the importance of monitoring actual and planned values, adjustments and ensuring objective achievement as well as the close link between project steering and project management.
The differences lie in their methodology and scope: While in DIN 69901 project steering is merely regarded as an operational component, in PRINCE2 and the PMBOK Guide it is regarded as an integral part of a more comprehensive project management. PRINCE2 is more process oriented and structures steering into clearly defined phases, while the PMBOK Guide offers more flexibility through a modular approach.
For small to medium-sized projects with clear framework conditions, DIN 69901 is well suited, since it offers a practical and easily applicable orientation. PRINCE2 is ideal for more complex, inter-organizational projects, since it strongly relies on processes and clearly defined roles. The PMBOK Guide is particularly suitable for projects that require a high degree of customization and integration, such as project steering in construction or IT projects.
Companies benefit from established project steering standards, since they provide clear guidelines for planning, monitoring and controlling of projects. They facilitate the decision for a methodically suitable controlling approach that can be individually tailored to the specific requirements of a project. By using international standards, companies can also facilitate collaboration in interdisciplinary or multinational teams and assure the quality of their projects.
In the table below we summarize the description and area of application of the three project steering standards.
| Standard | Description | Area of application |
|---|---|---|
| DIN 69901 |
|
Universal projects |
| PRINCE2 |
|
Complex projects in regulated industries |
| PMBOK Guide |
|
IT projects, international proposals |
Project steering and project plan: is a project plan necessary?
A project plan is indispensable since it provides a basis for project steering. It defines planned values that are compared with actual values, such as schedules and resources that are required for successful implementation. The project plan provides clear orientation for all persons involved.
Without a detailed project plan, it is almost impossible to recognize deviations, measure progress or initiate control measures in good time.
The most important components of a project plan include:
- Milestones: They mark key interim goals in the course of the project and serve as checkpoints for progress monitoring. Milestones help to divide complex projects into manageable sections and allow you to identify delays or problems at an early stage.
- Schedules: They define the chronological sequence of tasks, phases and milestones. Schedules allow progress to be monitored and provide a basis for control, especially when adjustments or prioritization become necessary.
- Resources: They include personnel, budget and materials required to implement the project. A clear resource plan ensures that bottlenecks are avoided and existing capacities can be optimally utilized.
A well-structured project plan thus forms the backbone of project steering. It provides a clear basis for the adjustment of planned and actual values.
Project steering in the IT sector: what are the particularities?
The dynamic and complexity of projects in the IT sector lead to specific requirements for project steering. Here, controlling takes on a central role in tackling technical and organizational challenges and ensuring that projects are concluded cost-efficiently and in the desired quality.
The essential areas of activity of IT project steering include:
- Quality assurance: Focuses on compliance with development standards, tests and acceptance criteria.
- Scheduling: Adapts to iterative development processes such as Scrum or Kanban.
- Cost management: Includes both direct project costs and long-term maintenance costs.
Project steering accompanies all project levels: From initiation via definition, planung and controlling through to project conclusion. The solution is successfully put into operation upon handover.
Each phase requires specific control measures such as regular reviews, rsik analyses and coordination between developers, testers and clients.
Typical challenges in IT projects are changing requirements, technological complexity and communication problems between technical and non-technical stakeholders. Project steering tackles these challenges by using agile methods and specialized software tools that enable planned-actual comparisons and collaborative working.
Well-organized steering ensures that a project remains flexible without losing track of time, costs and quality.
What are the tasks in project management?
Project steering comprises a variety of tasks aimed at ensuring the success of the project. Here, the project steerer assumes a central role by acting as an operative control instance, coordinating processes and identifying deviations at an early stage.
Despite these diverse tasks, project steering focuses on three core areas:
- Time management: The project steerer ensures that all tasks are completed on time. This includes the creation and maintenance of schedules, the definition of milestones and the regular review of progress. Delays are recognized at an early stage and measures are initiated to ensure that the schedule is adhered to.
- Cost management: In cost management, the focus is on controlling the project budget. The project steerer monitors the expenditure and regularly compares it with the planned costs. In the event of deviations, adjustments are made immediately in order to avoid budget overruns and minimize financial risks.
- Quality management: Quality assurance includes compliance with the agreed standards and objectives. The project steerer regularly checks whether all processes and results meet the requirements and ensures optimization where necessary.
Project steering is also the link to other project roles. While the project manager defines the objectives and makes decisions, the project steerer provides the necessary data and analyses to support these decisions. The project steerer also works closely with the project team by monitoring progress, identifying obstacles and proposing solutions.
What tasks does a project steerer perform?
A project steering is an independent role within the project. Alternatively, the project steerer can also take on the task of project management. Project steering plays a central operational role within a project and is the interface between the project participants.
The specific tasks of project steering include:
- Planning and coordination: Supporting and monitoring the implementation of the project plan and the assignment of work packages.
- Monitoring and control: Continuous review of planned values such as time, costs and quality compared to actual progress.
- Risk management: Identification of potential risks through analyses, scenario planning and impact assessment. Taking targeted steps to ensure the success of the project when deviations or risks occur.
- Communication and interface management: Mediation between the client’s requirements and implementation by the project team. Regular reporting on the project status to keep everyone involved up to date.
- Quality assurance: Review project results to ensure that they meet the defined standards and objectives.
Project steering ensures that clients, project teams and external partners collaborate efficiently. It translates the client’s strategic specifications into operative tasks for the team and ensures that feedback from the implementation is reflected in the planning process. This role requires a high degree of communication and organizational skills in order to resolve conflicts and avoid coordination problems.
Project steerers systematically analyze potential risks that could arise from delays, budget overruns or qualitative deviations. Risk management in projects is carried out using methods such as SWOT analysis, checklists or monitoring tools. Project steerers prioritize risks based on their probability of occurrence and their potential impact. On this basis, they develop strategies to avoid, minimize or manage risks.
Project steerers use different tools to accomplish their tasks efficiently, including:
- Project management software for time and cost plans as well as for progress monitoring
- Collaboration tools for coordination and collaboration within the team
- Analysis and tracking tools such as Earned Value Management and KPI dashboards for the monitoring of project key figures
- Risk management tools for the identification and evaluation of risks
Project controlling as part of project steering
Project controlling is a central component of project steering and makes a decisive contribution to ensuring that objectives are achieved. It focuses on monitoring time, costs and quality by comparing planned values with actual developments. Deviations are analyzed, documented and corrected through targeted measures so as not to jeopardize the success of the project.
The project steerer assumes operational responsibility for the implementation of controlling and works closely with the project manager. In many projects, however, these roles are combined so that one person assumes both steering and management and thus bears overall responsibility for planning, monitoring and implementation.
While the project manager bears overall strategic responsibility, the project steerer ensures that the controlling results are promptly translated into operational measures. Project steering and project controllingthus complement each other: Controlling provides the data and analyses, and the steering committee implements the necessary adjustments on this basis.
The following key figures are regularly monitored in project controlling:
- Degree of completion: Specifies the proportion of completed work in relation to total work.
- Planned-actual deviation (time): Comparison between planned and actual time values.
- Planned-actual deviation (costs): Comparison between planned and actual projects costs.
- Earned Value (EV): Measures the value of actually performed work in relation to the planned costs.
- Cost Variance (CV): Difference between Earned Value and actual costs.
- Adherence to deadlines: Monitoring milestones and deadlines.
- Quality key figures: Metrics for evaluating whether defined quality standards are achieved.
By using these key figures, project controlling provides the transparency required to reliably evaluate the project status and make well-founded decisions.
What project steering tools and features are there?
The efficient steering of projects requires the use of suitable tools and features that optimally support planning, monitoring and reporting. A central instrument of project steering is a comprehensive project management software (PM software) that integrates all essential functions in one system.
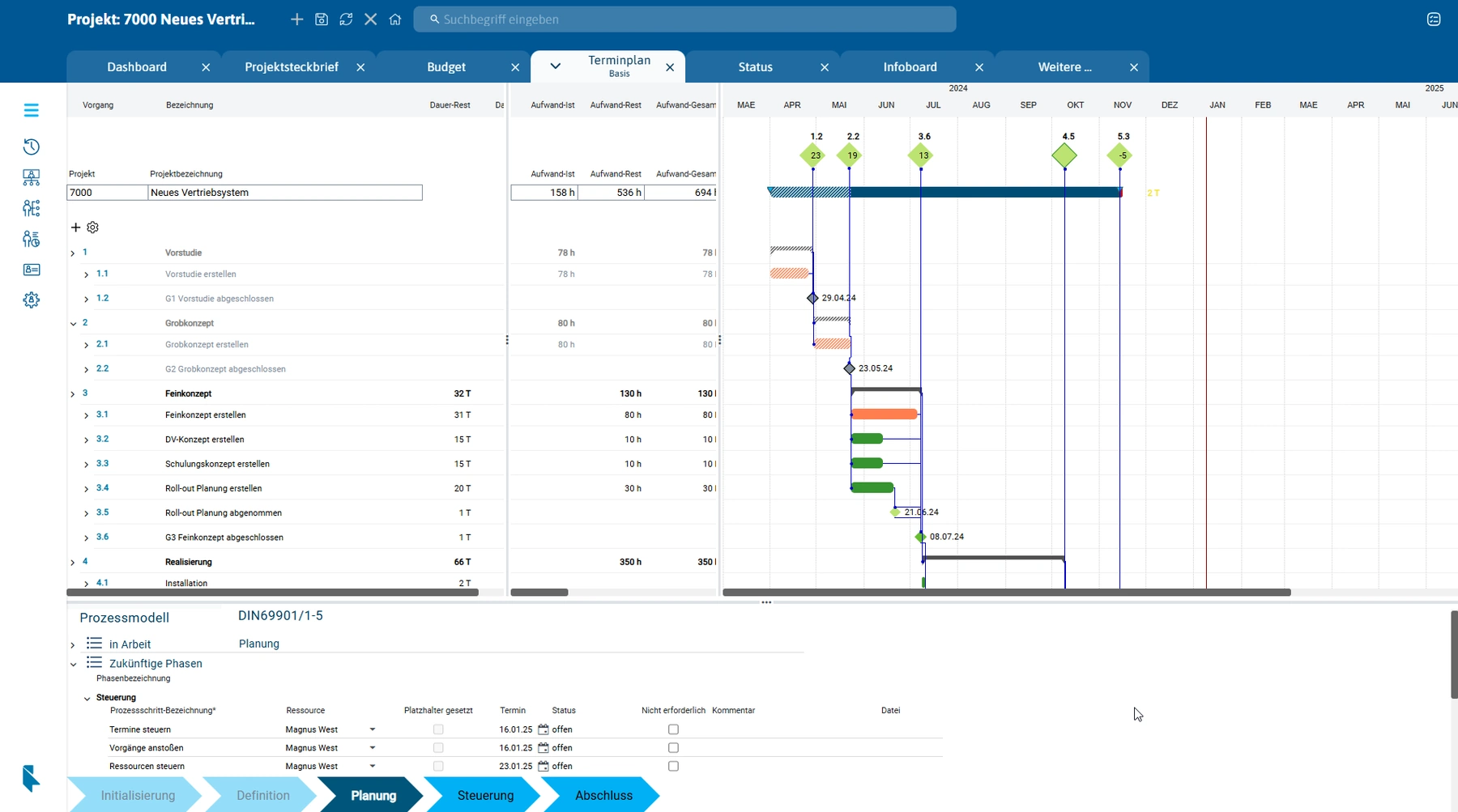
PM software provides a wide range of functions for coordinating planning, schedule monitoring, cost controlling and resource assignment in a central place. The value of these tools for extensive projects with many participants and complex dependencies cannot be overstated. Modern software such as PLANTA Project offers numerous features such as Gantt charts, work breakdown structures (WBS), resource management and AI-assisted functions.
The key features of PM software include:
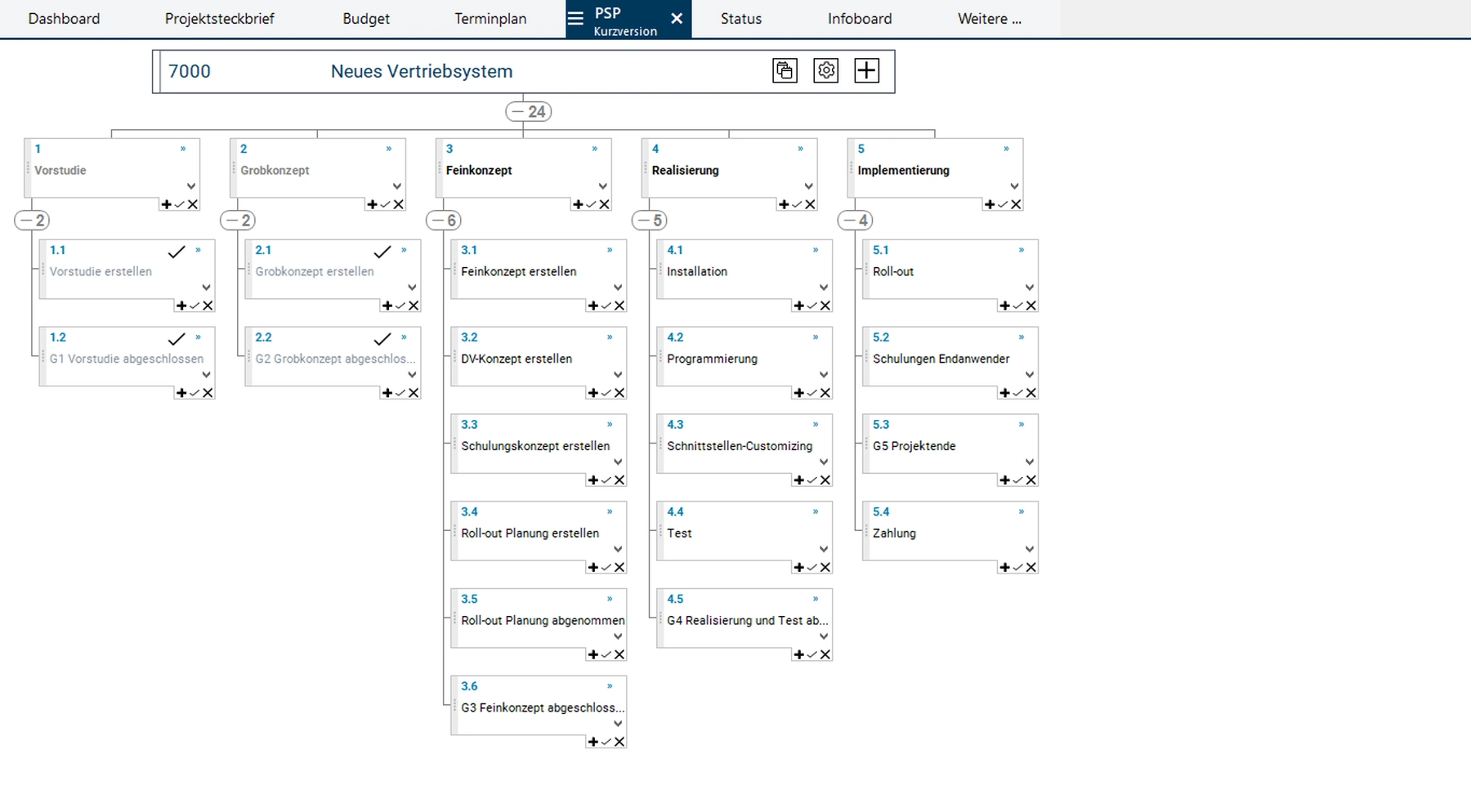
- Gantt charts: Visualize the chronological sequence of tasks, milestones and dependencies and enable precise scheduling and monitoring.
- Work breakdown structure: Divides the project into tasks and work packages and clearly displays dependencies and responsibilities.
- Resource management: Promotes efficiency through the assignment and optimization of resources such as personnel, material and budget and reduces bottlenecks.
- Cost management: Tracks project costs in real time, analyzes deviations, offers control options, facilitates budget control and saves costs.
- Schedule management: Plans and monitors key dates and milestones, including deadlines and buffer times, and reduces delays.
- Reporting: Generates reports and dashboards to represent the project status and progress visually and based on data. It increases transparency and improves decision-making.
AI-assisted tools can be used in complex projects with dynamic requirements to supplement traditional PM software. They provide support through automated analyses, forecasts and optimization suggestions. These functions offer particular advantages for data-intensive projects, such as IT or research projects, and enable more precise decision-making.
The following table provides an overview of proven project steering features including their advantages and disadvantages.
| Project steering tool / feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gantt charts |
|
|
| Work breakdown structure |
|
|
| Resource management |
|
|
| Cost management |
|
|
| Date management |
|
|
| Reporting |
|
|
| AI-assisted analyses |
|
|
What are innovative approaches in project steering?
Innovative project steering approaches include hybrid project management methods which combine traditional and agile approaches. Hybrid methods allow for flexible adjustments to specific project requirements by combining the stability of traditional planning methods (such as Gantt charts) with the agility and adaptability of methods like Scrum or Kanban.
Hybrid project management methods are used in projects that have clearly defined initial objectives but have to take changes or new requirements into account as they progress. One example is the combination of waterfall methods for the initial planning phase and agile approaches for the realization, e.g. in software development. Here, a fixed schedule can be set for the main objectives, while individual work packages are processed in an agile manner.
Innovations such as AI-assisted tools and big data analyses can support project steering. They enable more precise planning through data analysis, automatic identification of risks and predictions of time and cost trends. This significantly reduces manual effort, which allows to place a stronger focus on operational coordination and the management of deviations. This supports the project manager in preparing and implementing strategic decisions. Real-time dashboards and automation ensure transparency and faster decision-making processes.
Companies benefit from these innovative approaches in the following way:
- Flexible response to changes without losing the overview.
- Saving time and costs, since processes are organized more efficiently.
- Achieving better project results, since risks can be identifies at an early stage and adjustments can be made in good time.
- Improved collaboration through the use of modern collaboration tools and transparency in communication.
Hybrid methods and innovative technologies allow companies to realize projects in dynamic and complex environments in a more efficient and targeted way.
Whitepaper 13 Common Mistakes in PM
How to avoid various mistakes in your projects
Whitepaper Hybrid Project Management
Hybrid systems allow you to react more flexibly to any project situation than agile systems
What role does project management software play in project steering?
Project management software is an indispensable tool for efficient project control. It helps to optimize planning, monitoring and steering by providing central functions such as resource management, collaboration and real-time reporting. With suitable software, teams can standardize their processes, create transparency and identify deviations at an early stage in order to initiate countermeasures in good time.
High-quality project management software should offer the following functions:
- Resource planning: Effective assignment of personnel, budget and equipment to avoid bottlenecks and make optimum use of capacities.
- Collaboration tools: Tools such as chats, shared dashboards or document management for promoting team-collaboration and making information available in a central place.
- Real-time reporting: Automatic generation of reports on progress, costs and deadlines to ensure transparency for all parties involved.
- Date and budget management: Functions such as Gantt charts, milestones and budget tracking that allow to monitor schedules and costs.
- Risk management: Identification, evaluation and controlling of potential risks.
- Integration: Connection to other systems such as Jira, SAP or Outlook to seamlessly supplement existing workflows.
PLANTA Project presents an ideal solution for project steering and was acclaimed best software for project management 2024. It combines classic and agile methods and is suitable for project-driven teams in SMEs as well as large companies. The software also enables hybrid project steering.
Users benefit from PLANTA Project in the following ways:
- Extensive functions: The software supports multi-project management, Gantt charts, time recording, resource planning and controlling. Features such as budget management and workflow automation increase efficiency.
- Flexibility and scalability: Available as SaaS or on-premises solution, it easily adapts to individual requirements of any organization.
- User friendliness: The intuitive interface and supplementary tutorials make it easy to get started.
- Data protection: Made in Germany with GDPR-compliant servers, PLANTA offers highest data protection standards.
- Integration: Thanks to the PLANTA universal interface, companies can easily integrate systems like Jira, SAP and Outlook.
PLANTA Project offers companies the following advantages:
- More efficient organization of processes by centralizing planning and steering.
- Saving costs and time, since automations and clear workflows minimize manual effort.
- Increased transparency, which facilitates decision-making and communication with stakeholders.
- Using scalable solutions that are suitable for both simple and complex projects.
Combining functionality, user-friendliness and data protection, the PLANTA software is a powerful tool that takes project steering to a whole new level and ensures the long-term success of projects.
Conclusion on project steering
Project steering encompasses operative planning, monitoring and controlling of projects, to comply with requirements regarding schedule, costs, and quality. This role concentrates on the practical implementation and controlling of planned and actual values. Important tasks include the monitoring of schedules and budgets, progress control and risk and change management. Methods such as milestone trend analysis and earned value management as well as good project management software help to improve efficiency and transparency. Using the right tools and techniques is crucial in order to successfully complete complex projects in a targeted manner.
FAQ
Is it possible to combine agile and traditional project management?
Agile project management is based on the values and principles of the Agile Manifesto and can be combined with traditional project management to benefit from the advantages of both approaches. Clear structures and predictability meet flexibility and iterative working methods, which enables efficient adaptation to different project requirements.
For what type of projects is agile project management unsuitable?
Agile project management is unsuitable for projects with fixed requirements, strict schedules or highly regulated framework conditions such as the construction industry or aviation. Important metrics for measuring success are customer satisfaction, speed of completion (lead time) and adherence to budget and quality.
What industries use traditional project management the most?
Traditional project management is often used in aviation, in construction and in the automotive industry, especially for projects with long development cycles and extensive waterfall plans, e.g. up to model-readiness. However, even highly regulated sectors such as the pharmaceutical industry are increasingly relying on hybrid approaches in order to operate more flexibly.
Project Steering with PLANTA Project
The right project management software allows you to steer projects more easily.
This blog post has been translated by Julian Hammer
Related Posts
RECENT POSTS
Project Steering: Explanation, Tasks and Methods
Beate Schulte2025–04-07T12:43:59+00:004. April 2025|
10 Effective Methods and Strategies for Multi-Project Management
Beate Schulte2025–04-11T16:38:05+00:0013. March 2025|
Agile Or Traditional Project Management? Differences, Advantages and Disadvantages
Larissa Plank2025–02-27T14:27:57+00:0026. February 2025|
















